Computing devices like ours have both SRAM and DRAM at hand. Their primary function is to supply data to and from the processor.
Although they perform similar functions, they differ in price and speed. This is because of the way they operate and the technology used to manufacture them.

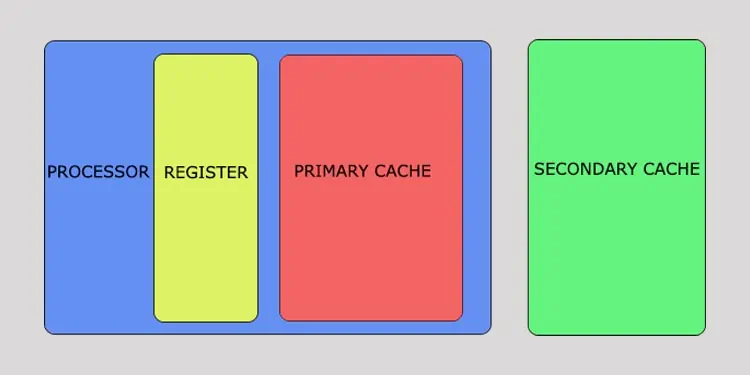
Static or SRAM modules come ascachesandregistersplaced between the processor and the Main memory. It is a superfast, low-density, more expensive type of memory. Data on an SRAM does not need to be rewritten as long as power is supplied to it.
Meanwhile, Dynamic or DRAM is the type of memory module we typically consider “RAM.” Present on the motherboard, it is a cheaper, high-density, and comparatively slower memory.
What is Dynamic RAM?
Dynamic RAM or DRAM is a type of memory manufactured using capacitors and transistors. This memory can hold datamore densely than an SRAM and is also cheaper to manufacture.
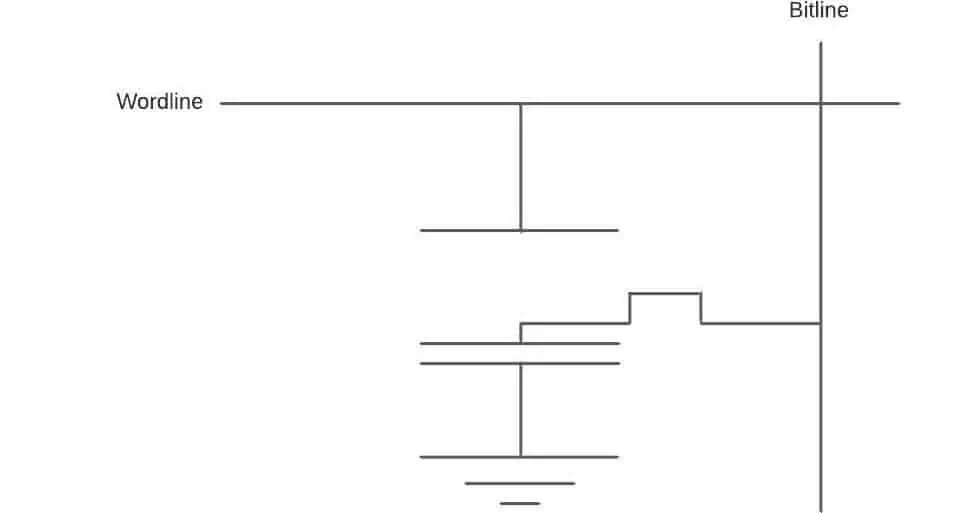
DRAM loses all its data when the system cuts off the power supply because it is a volatile memory. As its name implies, the Dynamic in DRAM means that data is written repeatedly to keep it, even when the power supply is constant.

Unlike SRAM, the determinant for speed and capacity of Dynamic memory modules aren’t based on their hierarchy level. Instead, their generation determines them. Thelatest being the 5th generationof DDR topology (DDR5 or Double Data Rate Fifth).
What is Static RAM?
Manufacturers useflip-flops and transistors to make Static RAM. This type of memory module can transfer data faster compared to DRAM. They are also much smaller than their Dynamic counterpart, being only acouple of Megabytes in size.
Static RAM is also a type of volatile memory, but due to the technology used to manufacture it, existing data in SRAM isstored without being rewritten. Instead, when new data comes in, the old data is overwritten, and the CPU then uses the new information for processing.

Static memory modules work on a hierarchical basis, meaning the fastest cache memory is theLevel 1 or L1 cacheand, after that, theLevel 2 or L2 cache, and so on.
Differences between Dynamic RAM and Static RAM
Technology Used
Both memory modules hold data for the CPU to fetch and process. Yet, how they do this task and the technology used to manufacture them differ.
SRAM stores the bits on a type of flip-flop known as alatch. Here, the data is stored in the form ofvoltages. DRAM, however, functions by keeping the data ascharges on a capacitor within a transistor.
These memory modules also come in various shapes and forms. DRAM, being a modular component,has more formswhen compared with an SRAM. The most common form factors for DRAM are
SRAM comes in the form ofcachesandregisters. These are memory modules that focus on speed above all. They arenot upgradable or swappableand are either integrated into the CPU or soldered to the motherboard.
Use Cases
Because of how they function, Dynamic and Static RAM are built for very different use cases.
DRAM is preferable when computing memory requireslow cost and high storing capacity. Thus, they function as the main memory for consumer-grade devices. SRAM, whereas, is used on components wherespeed is the main priorityand cost is a non-issue.
The main use case of DRAM is to hold large amounts of data that the processor needs to access. Because of the technology used to manufacture it, DRAM can pack transistors more densely than an SRAM’s latch.
SRAM functions as a buffer between the main memory and the processor. It stores information and instructions for the applications you use frequently which then enables the processor toaccess and load applications quickly.
Price
Dynamic and Static RAM use different technologies while manufacturing. SRAM, built from latches, occupies alarger physical spacethan DRAM, which uses a capacitor and a transistor for construction.
This requires a sizable amount of resources to construct an SRAM with the same data-holding capacity as a DRAM. Thus, most manufacturers install an SRAM with significantly less storage space to reduce product costs.
Verdict
The following are the major difference between Static and Dynamic RAM
Despite being cheaper, DRAM can hold more data but issignificantly slower. Because, in a DRAM, thesystem must constantly rewrite the data to retain it.
While much more expensive, using SRAM when speed is of concern is more preferable. SRAM alsotakes up more space to store the same amount of datawhen compared to a DRAM. These limiting factors then influence the manufacturers to determine the storage capacity of an SRAM.