Whether you want to protect your online privacy or access restricted content, VPN is the ideal choice. However, it’s frustrating when you may’t set it up properly, or the connection can’t be established leading to different error messages.
While incorrect credentials are a common cause, the VPN may also not work due to server or internet-related problems. Additionally, IPv6 incompatibility, failing Remote services or network protocols, corrupted WAN Miniport drivers, and blocked ports can also cause this issue.
Before moving on with the hard fixes, let’s start with basic troubleshooting.
General Troubleshooting Tips
Try Disabling IPv6
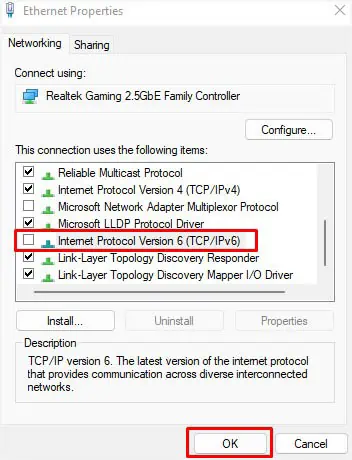
Whether you’re unable to connect to the VPN at all or can’t use the internet while being able to establish the connection, simplydisabling IPv6can sometimes do this trick.
Some VPN servers only utilize IPv4 addresses and headers and might not be compatible with IPv6.
Adjust MTU Size
If your VPN server supports IPv6, but you’re using large data payloads (watching live streams/broadcasts, transferring/downloading large files, etc.), this might add more space to the IPv6 header. This might be the reason your VPN keeps disconnecting.
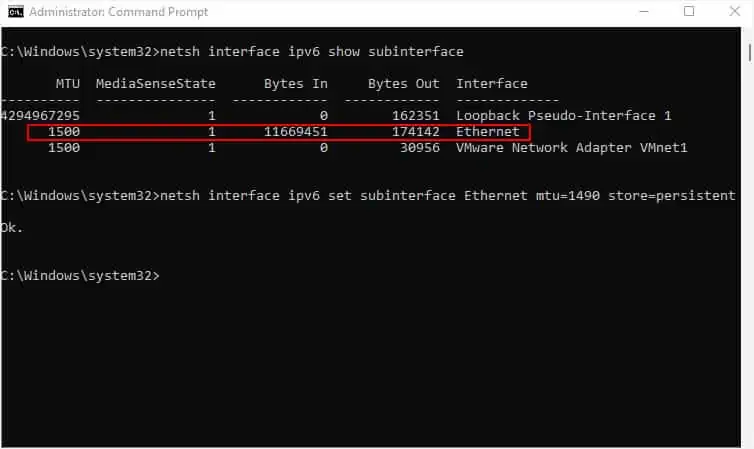
A simple workaround to this problem is to lower the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size. This way, the header space is well-managed, and there will be less packet loss and potentially no packet fragmentation. So, you can make the VPN start working without disabling the IPv6 address.
Note:Since the recommended lowest MTU size for IPv6 is 1280, I won’t advise you to adjust yours to less than that. If your VPN is still not working, reset the MTU size and know that IPv6 is probably not causing the problem.
Check for Network Adapter Issues
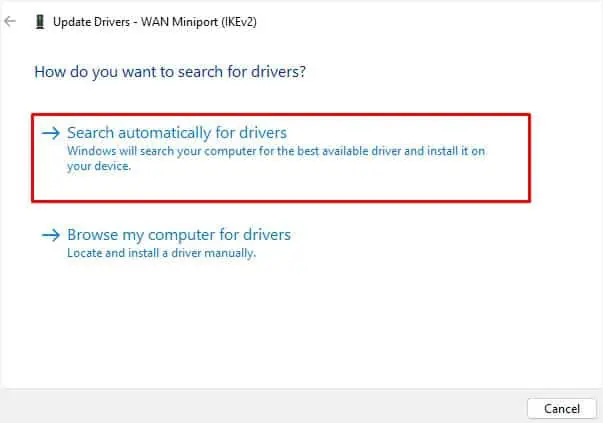
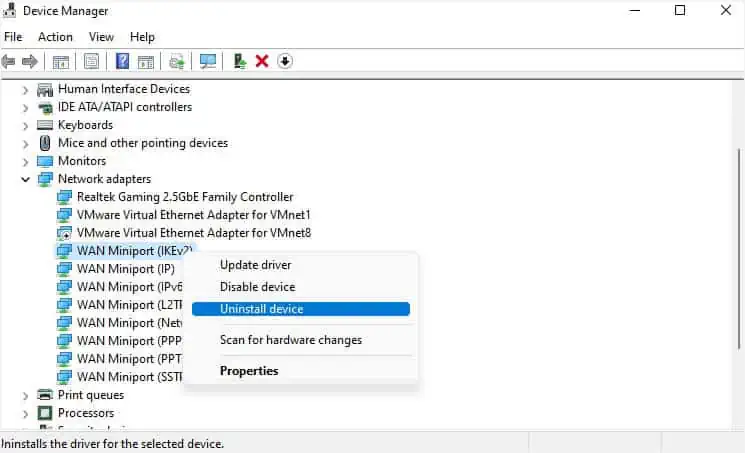
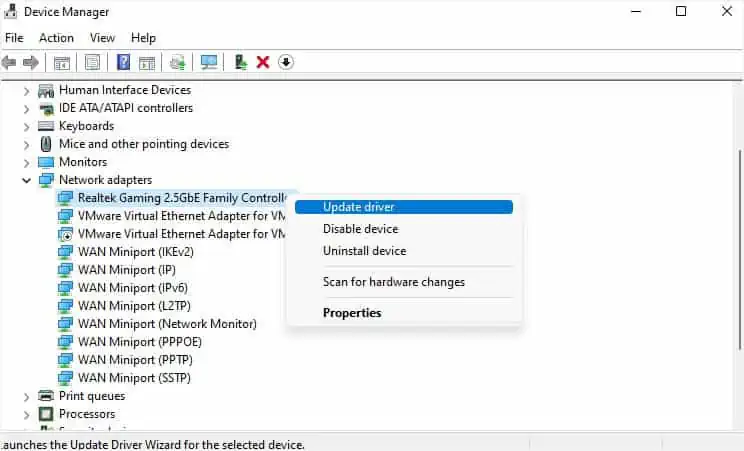
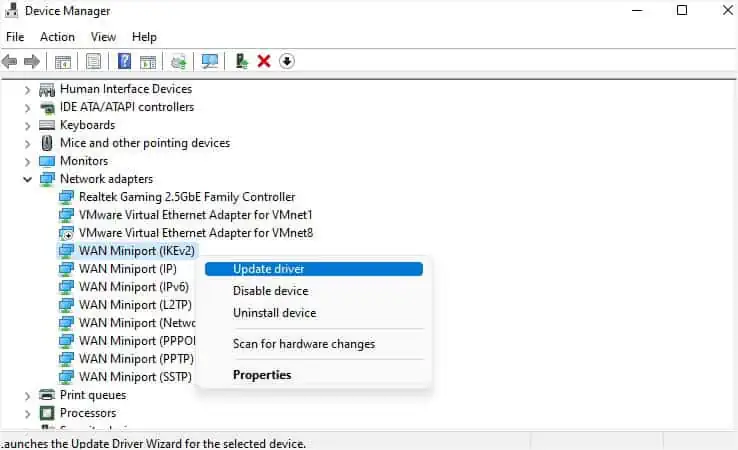
WAN Miniport device drivers provide alternative connection methods, including the VPN. If outdated or corrupted, your VPN might stop working or throw different errors.
To solve this, you’re able to either update (if possible) or simply reinstall them following the below instructions:
Open Blocked Ports
Based on the tunneling protocol used for establishing a VPN connection, it’s essential that the necessary ports remain open.
Here’s a chart that should help you out on which TCP/UDP ports your firewall shouldn’t block:
Setup Exception for UDP
If your VPN software utilizes User Datagram Protocol (UDP) instead of TCP, know that this is used for establishing low-latency and loss-tolerating connections. In case there are security problems, your VPN might stop working. If that’s the case, you can set up a UDP exception by introducing theAssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRuleDWORD in Windows Registry Editor.
Caution:Incorrect changes in the Windows registry can cause serious issues and you might even have to reinstall the operating system. To be on the safe side, I suggest keeping a backup so you may restore it if anything goes wrong.
Check Issues with the Remote Services
Remote Access Connection Manager (RDCMan) is a Windows service responsible for VPN connections from your computer to the Internet or other remote networks. If the service is not running or having issues, you might encounter VPN connection troubles. Here’s what you may do:
Try Flushing the DNS Cache
If none of the aforementioned steps worked out, there could be certain faults with the DNS Resolver Cache that could be responsible. Certainly, it’s a good idea to add new DNS entries byclearing the old ones. This way, your computer can send new DNS queries to the VPN server, possibly fixing the problem:
Disable Proxy Server
Generally,proxy serversare not needed for VPN connections. I do not think you have set it up yourself. But if you have unknowingly configured this, it’s better to disable it. Since most Windows users have fixed the problem this way, it’s worth a try:
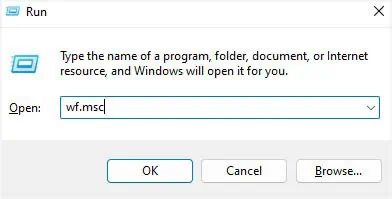
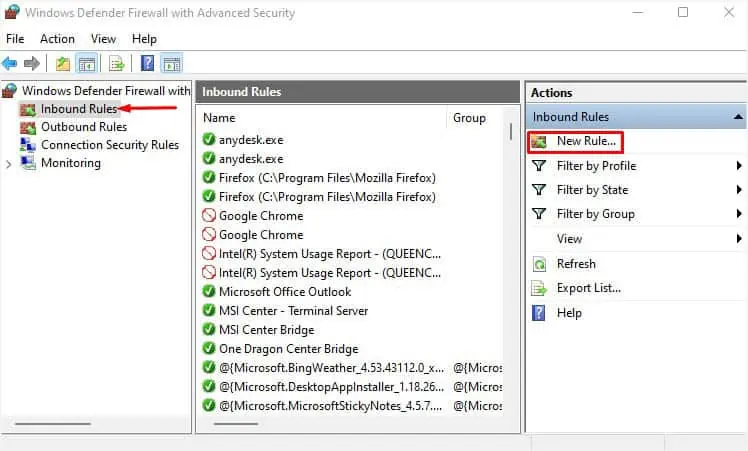
Allow Your VPN App to Pass Through the Firewall
As mentioned earlier, it’s better to adopt the Windows in-built VPN rather than relying on third-party applications. But if you have decided to stick with it, I suggest you check whether the Windows Defender Firewall (or a third-party firewall) is blocking the VPN connectivity.
If that’s the case, you need to allow the application to pass through the firewall, and here’s how:
Perform System Restore
If you have made any vital system changes intentionally or unintentionally, this might be another reason for your VPN to not work. Some users have complained about facing a similar issue after a recent Windows update. Whatever the case, you can try performing a system restore to see if this solves your problem:
If your VPN is still not working after trying out all the steps I’ve mentioned, do not hesitate to post your exact problem in the comment section below.