Physical to Virtual (P2V) operations are a critical part of server consolidation, and few solutions for this are as good as the ones from VMware. VMware vCenter Converter automates the conversion process, for the most part, allowing you to move workloads off physical machines to virtual environments easily.
One thing we must mention is that VMware last released vCenter Converter in May 2018 and officially dropped support for it in Dec 2019. As of Feb 2022, it was also made unavailable to download, citing security and reliability risks.
The good news, though, is that this hiatus is only temporary. Beta testing for the renewed version of vCenter Converter is already underway, meaning a full release of the new version isn’t far off now.
We’ll update this article when that time comes, but until then, you’ll be limited to performing the conversion on Workstation and vCenter Converter versions prior to Feb 2022 only.
Before You Start
Virtualizing a physical machine creates a snapshot of all the files and settings on the machine and exports them to a virtual machine. you’re able to use Workstation Pro or vCenter Converter Standalone to virtualize a physical Windows machine, but only the latter option will work in the case of a physical Linux or Mac machine.
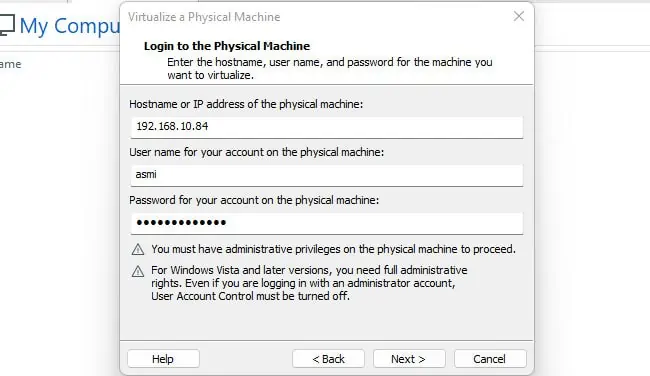
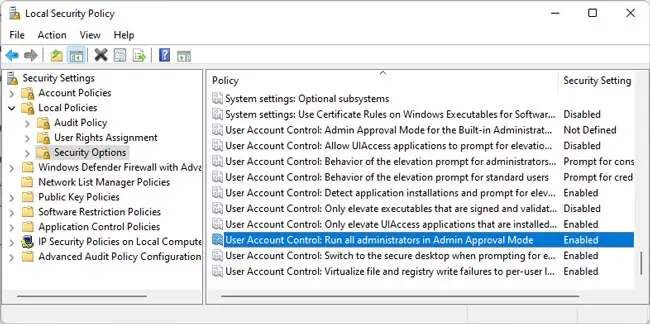
On the Windows machine, you’ll need an administrator account, and you’ll want to ensure that there’s network access. Next, you should temporarily disable the firewall withnetsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off. Additionally, you must also disable User Account Control (UAC). Here’s how you can do this:
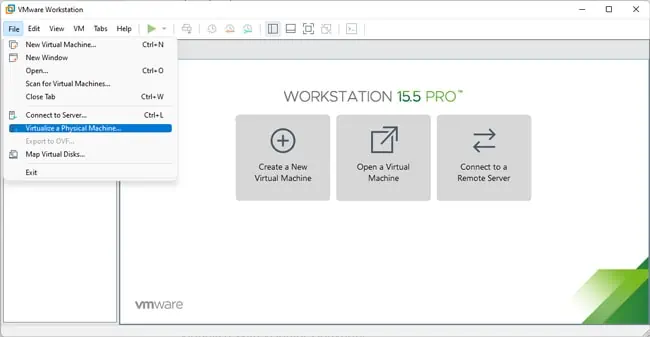
Virtualize With Workstation Pro
Do note that with Workstation Pro, you’ll have to virtualize the entire machine, while the vCenter Converter Standalone app allows you toselect specific partitions. With that said, on supported Workstation Pro releases, you can follow the steps listed below to virtualize a physical machine:
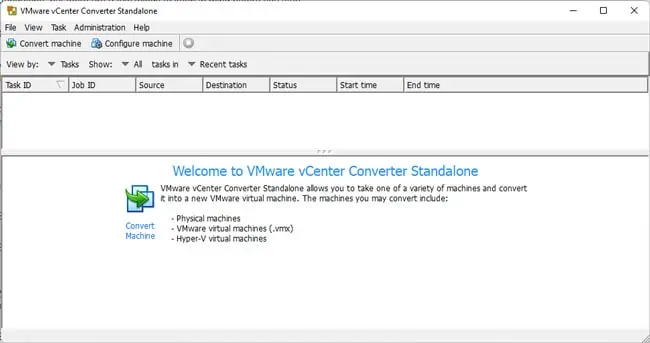
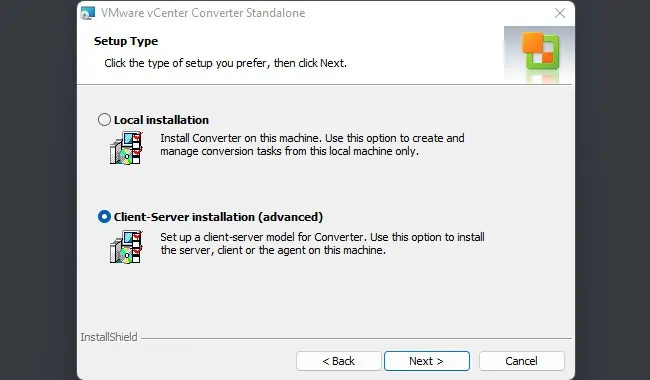
Virtualize With vCenter Converter
As stated, you can virtualize a physical Windows, Mac, or Linux machine with vCenter Converter Standalone, but there are a few things to keep in mind before you start:
With all that said, here are the necessary steps:
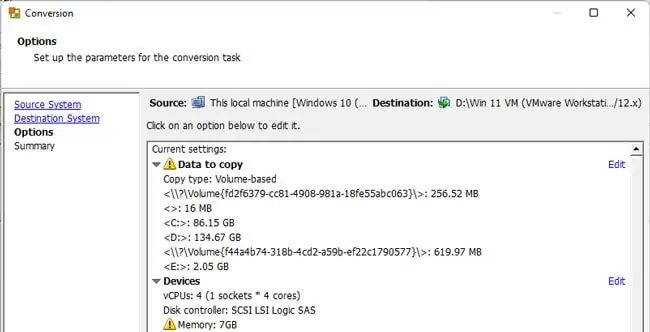
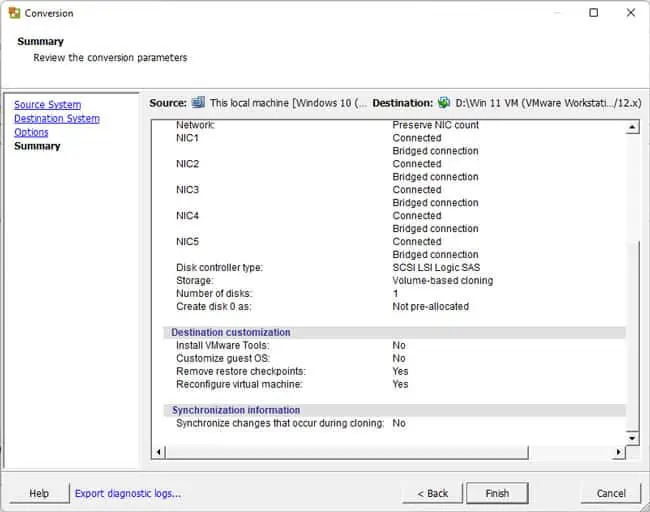
vCenter Converter Standalone will now copy the machine’s contents into a virtual disk file (.vmdk). Depending on the disk size of the physical machine, the conversion process will vary, but you can expect a few hours, atleast in most cases.
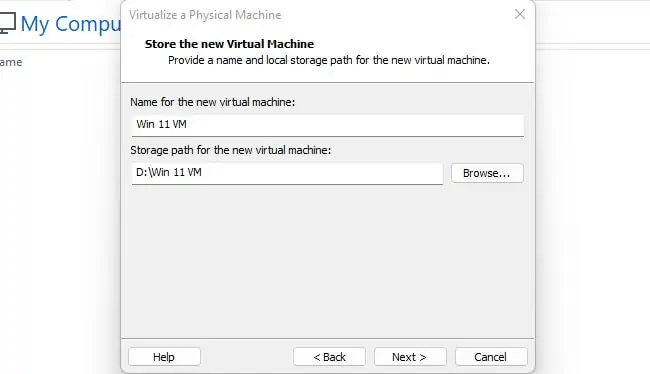
After the VMDK is created, you can use it to create a virtual machine. But once you do so, the files will be locked to that VM and not available to create other VMs. As such, you’ll want to create copies of the VMDK files if necessary. You’ll also want to ensure all the child VMDK files are in the same location and not scattered.

With all that said, here’s how you may create a Workstation virtual machine using.vmdkfiles: