The “Connection reset by peer” error occurs during a network connection when the other end or server closes the connection without reading the transferred data. The peer will return the data packet you sent while sending the RST (reset) bit and forcefully terminate the connection.
This issue usually happens if you are being blocked by the Firewall on any point in the route. But it can also happen due to other reasons. In this article, we mention different causes for the error along with how you can resolve it in each scenario.
Causes for Connection Reset By Peer
Here are some of the potential reasons for the “Connection reset by peer” error:
How to Fix Connection Reset by Peer
First, ensure your system is not too busy. If you have high usage of CPU, memory or network, you’ll experience issues while setting up a new connection.
Also, try restarting the session and retry the attempt to make the connection. Then move on to the possible solution we have provided below.
Most of the steps we have mentioned are fora Debian based Linux server. If you have any other system, you can apply similar steps by searching on the internet for the exact process. Some commands also vary between the different Linux systems. So look out for those as well.
Check Logs
First, you need to check the logs or error messages to narrow down the reason for the error.
If you have access to the server, you’re able to check the server-side logs as well.
For example, if you are experiencing this issue while setting up an ssh connection, you need to check the /var/log/auth.log file. To do so,
It shows the logging information sent by the SSH daemon during the authentication attempts of your remote system.
Check Internet Connectivity and Routing
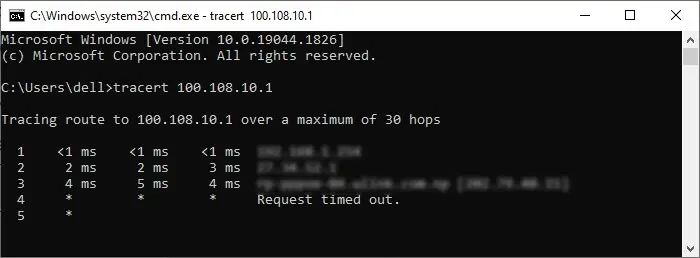
The next thing you should do is check for internet connectivity issues. You can check if the public or private server has gone down using IP lookup or similar websites.
you’re able to also use usetracerouteortracertto trace the route between the two endpoints and check which access point is resetting your connection. The syntax is:
If the public server or access points are down, you need to wait until they are up again. For issues with the private server, you can contact the system admin or restart it if you have access.
Check for IP Ban
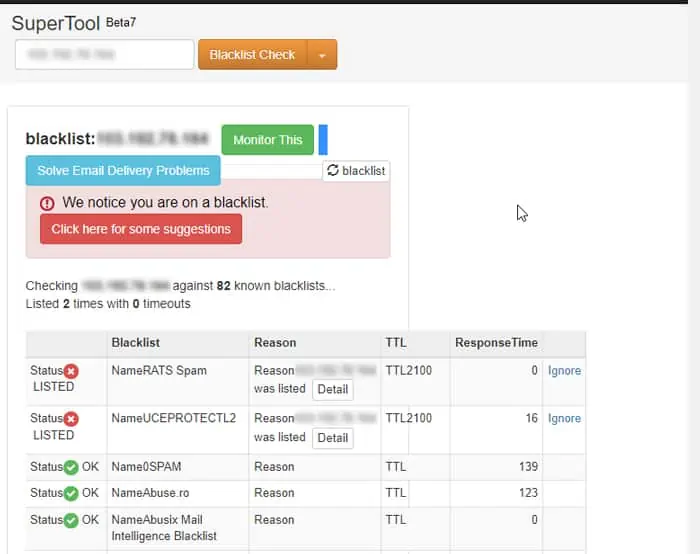
One major reason for this issue while connecting to public servers is your IP being blacklisted by major security service providers. Most public servers ban IP addresses while conforming to these server’s database.
To check whether your IP address is blacklisted,
If your IP is blacklisted on multiple security networks, or important ones like BARRACUDA, BLOCKLIST.DE, Nordspam BL, etc., most servers or security filters will also ban you.
The only thing you can do is talk your ISP and have them contact the server admin to remove the ban.
You can also trychanging your IP addressusing VPN to bypass this issue.
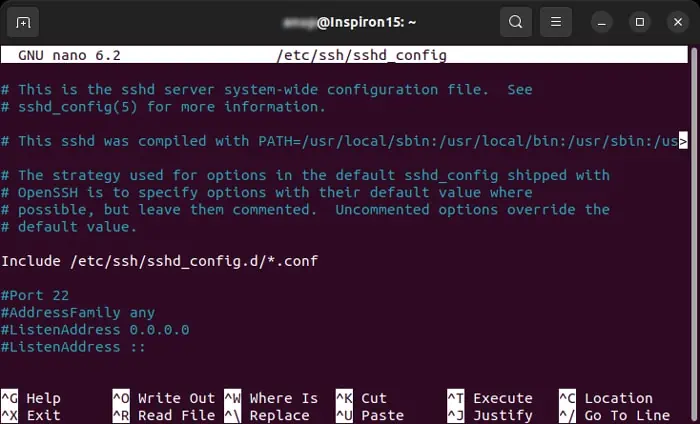
Check Firewall and Network Security Filters
The “Connection reset by peer” error occurs mostly due toFirewalls blockingaccess to the server.
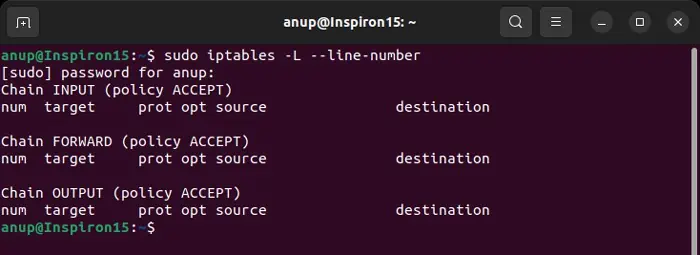
If you have access to the private server you are trying to connect to, you can check if the firewall is actually blocking access to your IP. To do so on Linux,
you’re able to alsocheck other security filtersavailable on the server. The steps may vary between the respective programs, so check the official website or documentation for the methods.
Then, you need towhitelist your IP addresson intrusion prevention apps like Fail2ban, DenyHosts, and so on, to make exceptions to the Firewall rules. The necessary steps to do so on Fail2ban is as follows:
Warning:Practices such as disabling Firewall or making exception for all IPs on the firewall is not recommended. Firewalls and security filters exist to protect your system. So rather than compromising the security, it’s better to search for a workaround.
Restart Services and Daemons
If you encounter this issue on a private network, it is possible that the server admin has changed the rules for the connection without restarting the daemon services. This causes the service daemons to get stuck as it is still want to conform to the previous settings.
For instance, if you are setting up a FTP connection using samba share, you need to use the commandsudo systemctl restart smbd. Since SSH service is available on almost all distros of linux, you don’t have to install any service package for it. So, for SSH connection, the command issudo systemctl restart ssh.
And if you are using any other hosting services to set up the connection, you need to restart their daemons as well.
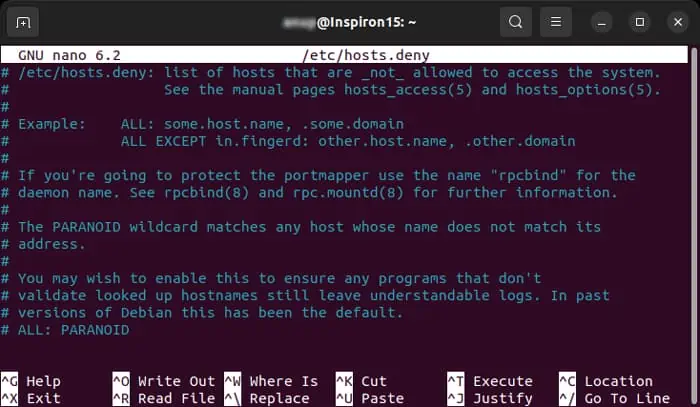
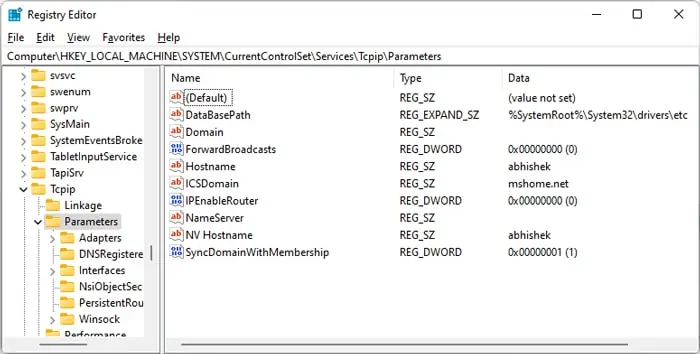
Edit Hosts File
Hosts files allow you to permit or deny access to particular IP addresses or hostnames. If you have access to the server, you should also check these files and make sure your IP address can establish a connection to the server.
To do so for a Debian System,
You can alsoadd your IP addresson thehosts.allowfile to force the connection. The process is similar to the above.
The daemon for FTP is usually vsftpd and for ssh, scp, and sftp is sshd. So, to allow ssh connection with local address,10.10.10.8, you need to addsshd : 10.10.10.8 , LOCAL
It is also possible to edit the hosts file on Windows based server. You can refer to out article on editing hosts file on Windows for more to learn the necessary process.
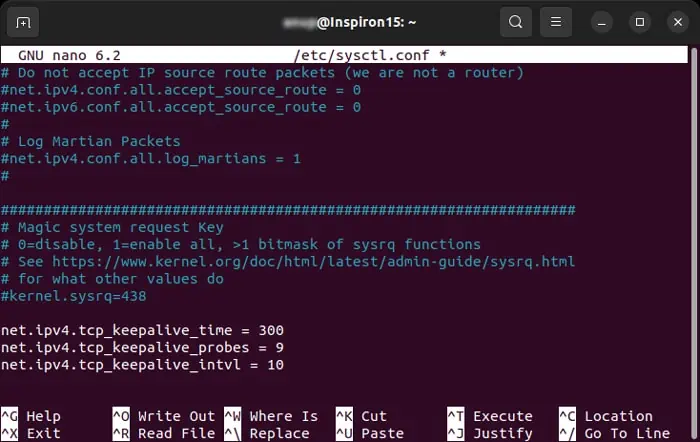
Increase Timeout or Send Keepalive Packets
Many networking tools drop idle TCP and FTP connections after a certain period of inactivity.
There are two ways to prevent this issue:
The first option is not a good solution. Keeping the timeout long can affect the server’s connections to other networks as they have to wait longer before attempting to set up a connection. You also need to increase the timeout on both ends, which is not always possible.
So, the better solution is tosend regular heartbeat or keepalive packets. This prevents the connection from being idle and keeps the session alive for longer period.
Some connections allow sending keepalive packets but you have to enable this process for others. Here’s how you’re able to enable the process of sending such packets:
On Linux
The above lines specify that the system waits for 300 seconds before sending the first keepalive packet. Then, it keeps sending the packet every 10 seconds. If it doesn’t receive ACK (acknowledgement) signal for 9 successive times, the connection is dropped.
Increasing the Keepalive period for SSH connections might compromise security as it remains open for a longer time. This connection is supposed to be very secure, so it’s not recommended to make any changes to the keepalive settings for ssh.
On Windows
Check sshd_config File
The sshd_config file configures all settings an SSH (Secure Shell) connection uses. So, if possible, you need to check this file on the server and make sure everything is alright.
Some of the options are:
MaxStartups
The MaxStartups value determines the maximum number of possible unauthenticated connections to the SSH daemon before the connections start dropping.
It has the formatMaxStartups 10:30:100, where,
If your remote client needs to make more number of connections concurrently, you need to change these values.
Subsystem sftp
On a secure FTP connection using openssh package, the default value of Subsystem sftp is set to/usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server. However, sometimes, the openssh binary is available at/usr/lib/ssh/sftp-serverinstead. So you can alter this value and check if it works. If it doesn’t, revert it to the previous path.
ClientAlive
ClientAlive is a more secure keepalive setting. you may change the ClientAliveInterval and ClientAliveCountMax values in sshd_config to enable this setting.
ClientAliveInterval determines the interval of inactivity after which sshd sends an encrypted message to the client. And ClientAliveCountMax determines the max number of times sshd sends this message before dropping the connection if it doesn’t get any response.
Check Support for SSL
If the host server has enabled SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) but you haven’t enabled this service on your end, you can’t establish a connection.
So, you need to check the support for SSL on your TCP or any other network client and enable it. If it doesn’t support SSL, you need to use another client.
You also need to check your certificates and make sure you don’t have any malformed keys or certificates.
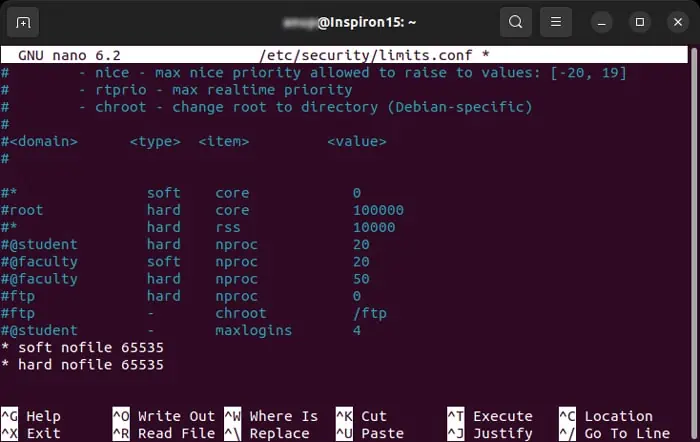
Change Open Connection Limit
Establishing a network connection also creates a socket, which is the logical window the client uses to communicate with the server. However, a server has a limit on how many sockets it can open at the same time.
If the server has already reached this limit, any new connection causes the server to drop the idle old connections. You can refresh or restart the session to renew the session. However, you can also increase the limit on the server side to facilitate more open connections.
If you want to change the limit for only the current session, you can use the commandulimit -n 65535, while replacing the number depending on your requirement.
To change it permanently,
For Debian and Ubuntu systems, you need to enable PAM user limits as well. To do so,
Debug Your Scripts and Configurations
Many users have encountered this issue while creating their own connection applications. In such scenario, any bugs in the scripts or configuration that unnecessarily close the connection or don’t conform the connection with the protocol will cause this error.
So, we recommend carefully looking through the program. Some protocols havequit or close commandsthat makes the host server close the connection.
You also need toclose all forked child processesbefore exiting to prevent zombie processes. The zombie processes stay in the process table even after terminating the child. If there are too many zombie processes, the process table gets full. This way, the system fails to create new processes, disrupting the connection.
If you have trouble debugging your program, we recommend getting help from technical forums such as stackoverflow while providing the source code.