PowerShell provides advanced options to control and manage all processes on your system. So, if you wish to automate any process or a bunch of them, PowerShell is the way to go.
Unlike Command Prompts, PowerShell uses cmdlets. These cmdlets are not standalone executables but process inputs from one pipeline and give output to another for the same object. So, you can use a number of cmdlets for the same object and have them execute as a single task. This property makes automating PowerShell scripts extremely effective.
If you want to know how you can automate PowerShell scripts, this article should provide you with all the necessary information.
How to Automate PowerShell Scripts?
Depending on your system, you may not be able to run PowerShell scripts on your computer. This is because PowerShell includes a setting called execution policy to protect your computer by imposing a particular level of restriction on such scripts. And most systems have this setting enabled by default.
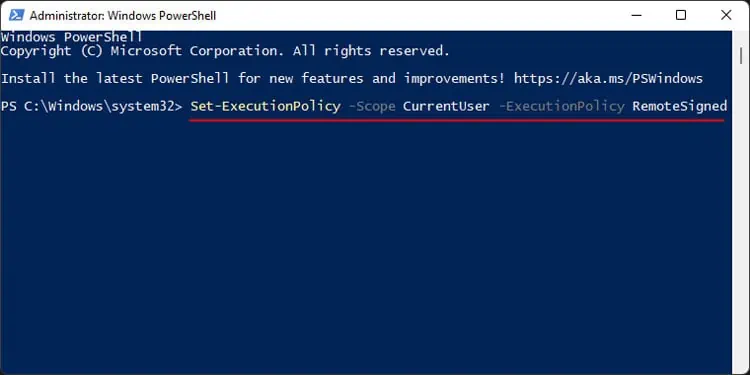
So, before automating the scripts, you need to remove or lower the restriction. First, open PowerShell as admin and enter the following command:Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
If you need to run unsigned scripts from the internet or external source, you need to use the following command instead:Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
Then, use one of the methods below to automate PowerShell Scripts on Windows:
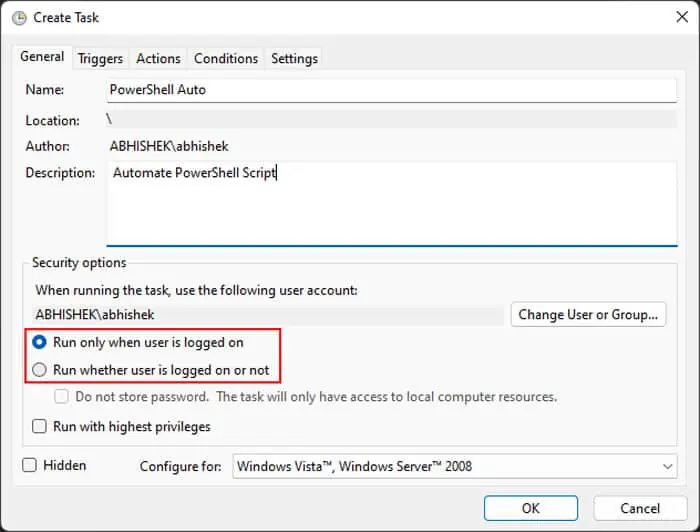
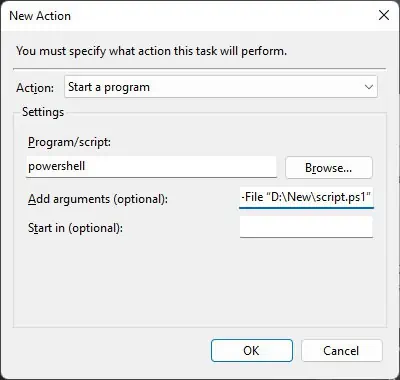
Using Task Scheduler
The Task Scheduler graphical tool provides an easy way to automate PowerShell scripts. It is the best option if you want to schedule a script you downloaded or got from an external source and don’t have much idea on how to use PowerShell.
Using PowerShell
If you are familiar with using PowerShell for scripting, the easiest method to automate any scripts is by actually creating a scheduled task through PowerShell itself.
First, we discuss the cmdlets you need to use to create such schedules. If you already know what they are, you can skip ahead to the main steps. Otherwise, you’ll need to go through these to understand how to execute the process.
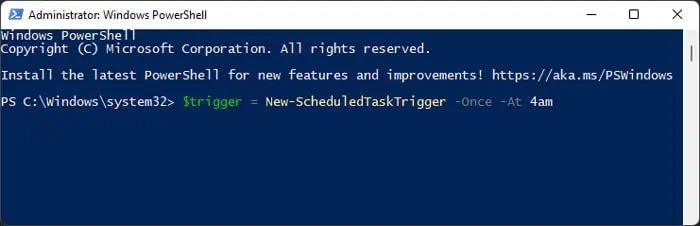
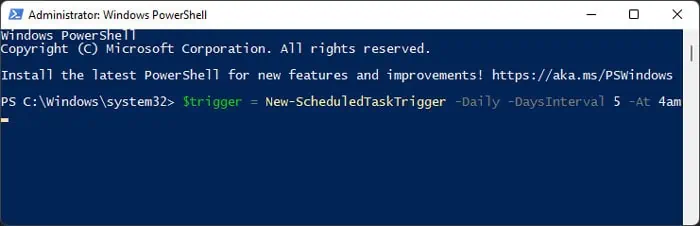
New-ScheduledTaskTrigger
It creates a trigger object for specifying when to schedule the task. You need to assign this cmdlet to a variable to create a trigger object.
You can use the following attributes with this cmdlet to trigger a task at regular intervals:
If you want to run the task at startup, you need to use the -AtStartup attribute. Similarly, you need to use -AtLogon to run tasks at user logon. you’re able to use the -User attribute to specify the exact user account.
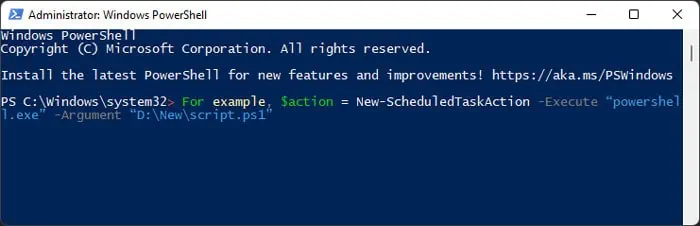
New-ScheduledTaskAction
It specifies which application you wish to run. You also need to create a task action object by assigning it to another value if you wish to register the task on your computer.
The main attributes you can use are:
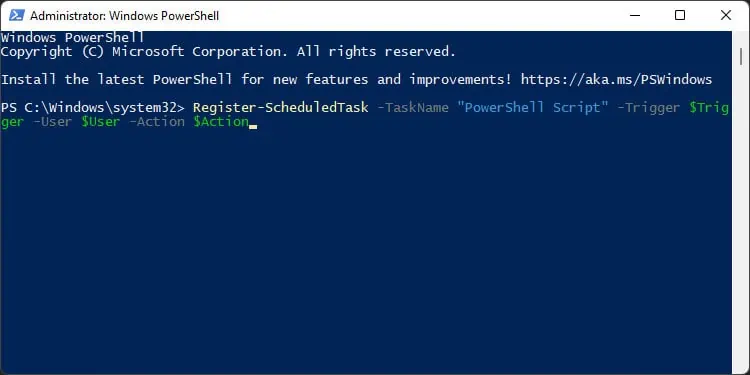
Register-ScheduledTask
It registers the task on your local computer. You need to use the objects you create using the cmdlets above in the arguments of this cmdlet to automate the PowerShell scripts. The necessary attributes are:
For example,Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName “PowerShell Script” -Trigger $Trigger -User $User -Action $Action

There are many additional cmdlets you can use for this purpose as well as attributes you can use with them. Since they are optional and not relevant in most cases, we haven’t included those here. But you can still visit theirdocumentation on Microsoft’s platformif you want to learn more about them.
Finally, here’s how you can use these cmdlets to automate PowerShell scripts: