The SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error indicates that one of your system processes encountered an exception error and crashed as a result. You may also see the BugCheck StopCode 0x0000007e in the BSOD error message.
This issue can happen if there are some bugs within the system processes—especially device drivers. But it is also possible that your hardware devices are faulty and could not handle the necessary operations. So, you need to find the necessary process or device and then resolve the issue.
Analyze Using a Debugger
Usually, the above BSOD error shows the system file that caused the crash along with the error message. If not, you need to first determine which file it is.
After knowing the system file responsible for the error, you can determine which device driver it relates to by looking at its Properties. Apart from drivers, some apps may also be responsible in very rare cases.
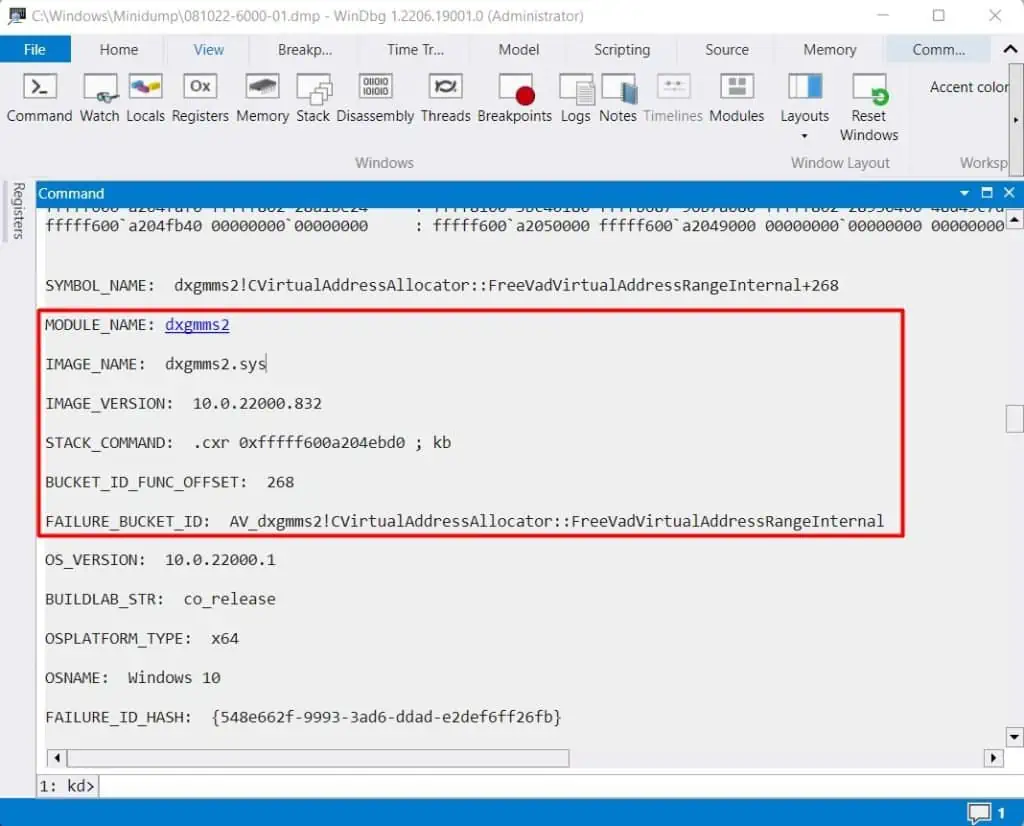
You can use the WinDbg debugger to analyze the error and look for the exact cause.
If the file is not there or you want more information, I recommend checking the internet.
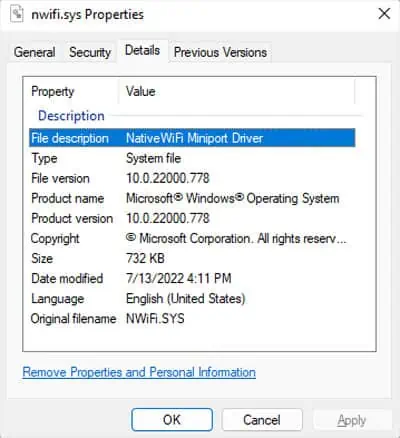
If an application is responsible, not the driver, then updating oruninstalling the applicationshould fix the issue. But if the analyzed file points to a driver, either the driver or its corresponding device may be faulty, so you need to troubleshoot for all cases using the successive solutions.
Check Compatibility With Device
If you started encountering the issue after upgrading Windows, your system may no longer be compatible with one or more hardware devices. Similarly, if you have just added new hardware to your computer, then the hardware may be conflicting with your system.
You can check the specifications of your system as well as the devices to look for any compatibility issues. You will find the device specifications on the manufacturer’s official website. Then, to check Windows specifications, you need to go to the relevant Microsoft web pages forWindows 10orWindows 11system.
If there is any incompatibility, you may need to replace the devices with compatible ones. You can also contact the device manufacturer or visit official forums to look for any other device-specific solutions.
Troubleshoot for Driver
After ruling out any potential conflicts with the system, the next step is to troubleshoot driver issues. First, tryupdating the driver.
We recommend searching for the device driver on official websites, downloading the latest version, and then installing it. But you can also use the Windows Update feature if it is a Microsoft-registered driver.

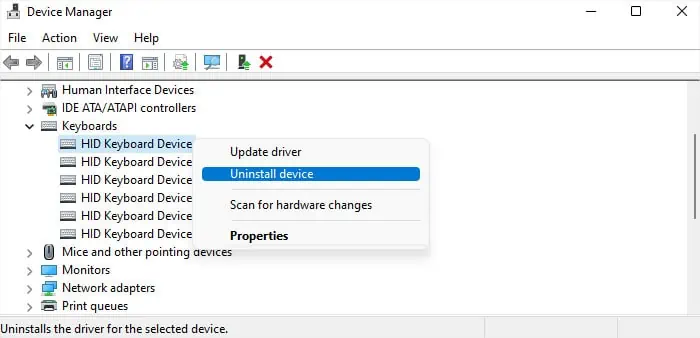
If no update is available, you need to reinstall the driver.
If it’s a graphics driver like NVIDIA, you need touninstall it with Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU)to completely remove any residual files and then install the latest version.
Sometimes, this error can also arise from conflicts between the devices and your BIOS or OS. In such situations, you may need toupdate your BIOSor the device firmware. You can similarly check the manufacturer’s website, download the corresponding setup files and run them for this purpose.
Disable Overclocking
You will also encounter various BSODs if you have overclocked your PC beyond the limit it can handle. In fact with all the powerful GPUs and CPUs out there nowadays, overclocking is no longer recommended and most people prefer upgrading the components instead.
So, if your CPU or GPU is overclocked, you should disable it and see if it helps. In case you used some third-party apps for overclocking, you can similarly use the same app to disable it. Or you can uninstall the app altogether.
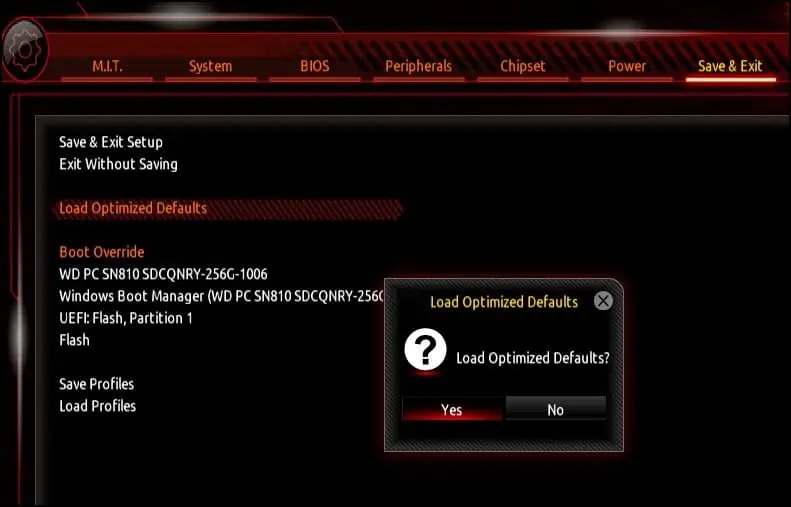
If you manually changed the voltage or frequency settings on the BIOS, you canreset the BIOSto do the same.
To reset the BIOS,
If you may’t access the BIOS setup, you canremove and reinsert the CMOS batteryas well. Also, some computers have a dedicated button on the motherboard to clear CMOS that you need to press for a few seconds.
Perform System Restore
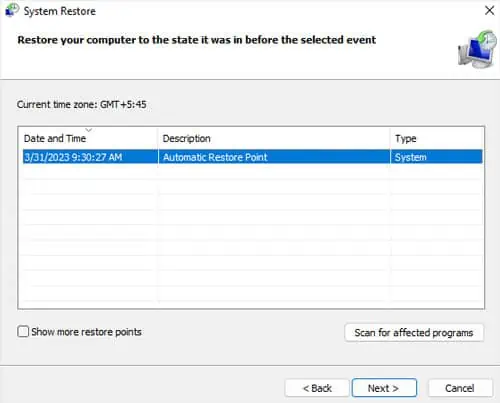
If you started encountering the issue right after making some changes to the system, you can run System Restore to revert your system back to the unaffected state.
Some possible changes include updating a driver or your system updates, installing an application, or running any third-party scripts. It is also why I always recommend creating a restore point before running such processes.
Run Hardware Diagnostic
You should also look out for any physical hardware issues with the corresponding device components. If your computer contains dedicated diagnostic programs on the BIOS or pre-boot environment, you’re able to run them and look out for potential issues. If not, you can use some third-party programs to run the diagnostics in an offline environment (without logging in).
Apart from that, issues with the RAM can also lead to different types of BSODs where the system or the debuggers detect some other apparent cause instead. You canrun the Windows Memory Diagnostics programto look out for such errors.
If the programs detected any errors, you may need to replace the relevant hardware device. If not, it still indicates a software issue. So, your only remaining option is toreinstall Windows.