Whenever you try formatting a disk or a volume, one of the choices you get is the File system on the drive. On Windows, you’ll get a choice between NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT.
FAT32 and exFAT both represent FAT file systems. NTFS is Microsoft’s proprietary file system developed to overcome all the limitations of the FAT32 file system. Although NTFS superseded FAT32 in the 1990s, the latter is still used a lot even today.
Both file systems differ in properties and working mechanisms. Let’s find out in detail.
What is FAT32?
Microsoft introduced FAT32 along with Windows 95 in 1996. It is the last of the unextended FAT file systems after FAT12 and FAT16 and was used for all storage disks before the development of NTFS. Now, it is only used in small solid-state storage devices likeflash drives.
All FAT file systems use an index table called File Allocation Table (hence, the name) to determine the location of all files stored in the drive as well as the available storage space. A FAT volume, including FAT32, actually contains the following components:
The system creates a File Allocation Table for a drive when formatting it to a FAT filesystem. FAT32 uses a 32-bit FAT entry, and it classifies each cluster in the volume as:
It also includes other information like thenumber of the next cluster associated with the fileand reserved areas on a disk. The drive also stores a backup of the table for recovery purposes.
Accessing and Storing File in FAT32
The Root Folder only contains information about the starting cluster of a file. So whenever you try accessing a file, your system needs to look up this table to keep checking the numbers of the successive clusters until it reaches the last cluster of the file.
The FAT32 file system regards the other folders and sub-folders as special files with their respective path entries. This way, it can use a similar process to access the files within them by using the data inside the components, other folders and files and the FAT.
While storing a file on a FAT32 drive, the file system searches for an unused cluster and saves the file in that cluster. If the cluster does not have enough space, it will search for other clusters to hold the remaining data of the file. It will also update the cluster information in the File Allocation Table while storing the data.
What is NTFS?
Microsoft released the first version of NTFS as the disk file system for Windows NT 3.1 in 1993. Since then, it has long succeeded FAT as the default file system for internal drives.
Like FAT32, the New Technology File System (NTFS) also uses an index table, Master File Table (MFT), to determine the file locations and available storage areas. The components of an NTFS drive include the following:
Unlike the FAT, MFT also stores a lot of information regarding file attributes, such as security descriptors and log files, which helps your system maintain all the advanced features that NTFS drives provide.
Accessing and Storing File in NTFS
The process to access a file is similar to that of FAT32. It uses the data in the MFT along with the File System Data to determine the location of clusters containing the file.
The difference is in the index records the file system needs to go through to access the file. NTFS stores records for small folders and large folders separately. The MFT stores all the records of small folders. On the other hand, the file system organizes large folders in B-tree structures, and the folders themselves contain the file records that the MFT structure can’t store.
NTFS uses this B-tree structure to index or group all similar file names so that the file system does not need to access all the file names while searching a file.
The process of storing a file is slightly different in NTFS drives. The file system first keeps creating records about the file in the MFT that contains the location of possible clusters that can hold the file.
If it finds a group of contiguous clusters that can store the complete file, it will use this space to store it. If not, it will still try storing the file in as few cluster groups as possible. Then, it will update all the remaining data in the MFT.
How are They Different?
Now that we know what FAT32 and NTFS drives are, let’s delve into the exact differences between these file systems.
Compatibility with Operating Systems
Compatibility is basically the only aspect where FAT32 reigns supreme over NTFS. It is the main reason why FAT32 is still very much popular.
Volume and File Storage
FAT32 comes with some major size limitations compared to NTFS regarding the partition as well as the individual files.
Partition or Volume size
Number of Files
Fault Tolerance
NTFS file system is ajournaling file system. It means that whenever you modify any contents in the file system, it can record all the changes it will be making as log files in a separate space before applying the changes.
So, if you encounter any system failures or crashes during the modification, the system can read that data and revert the incomplete changes.
FAT32 does not have such fault tolerance features. So, if a crash interrupts such processes, the file system will keep implementing incomplete changes, thereby resulting in data corruption.
NTFS also regularly monitors corruption issues and attempts to resolve them even when the volumes are online. If Windows detects any bad sectors (due to read/write failure or CHKDSK), NTFS will reallocate the data within the sector or cluster somewhere else and mark it as bad or unavailable. FAT systems lack any such recovery options.
Performance and Speed
While it may seem like NTFS is slower than FAT32 due to the journaling process, it is not usually the case. Most of the metadata, including the MFT on the NTFS drive, is already loaded to the cache when Windows starts. So, in practice, it does not need much time to read data from or write data to the MFT and the drive.
Also, in NTFS, large folders are stored in a B-tree structure that indexes similar file names together. So, unlike FAT32, it does not need to scan all file names whenever you try accessing a file.
As FAT32 does not perform journaling and there is more risk of data loss, most systems do not cache much data from a FAT32 drive. So, the system has to load the FAT table to the memory every time and update it.
So, for larger files, NTFS is the faster option. The FAT file system’s performance will also steadily decrease with an increase in the Volume size.
However, if you need to transfer or modify a lot of very small files, NTFS ends up being much slower due to the journaling.
Fragmentation
Whenever you attempt to store or move/copy a file to FAT32 hard drive, the file system will start saving it in the first unused cluster regardless if there are contiguous clusters that can hold the complete file. So, the file canget fragmentedmany times in different random clusters.
On NTFS hard drives, however, the file system itself first checks if there is enough space in the same area to store the file. If it finds this space, it will store the whole file there. It will only store the file in a non-contiguous space if it can’t find such space.
So, while enough contiguous clusters may not always be available in the same location, on a whole, NTFS doesn’t suffer from as much fragmentation as FAT32.
Compression
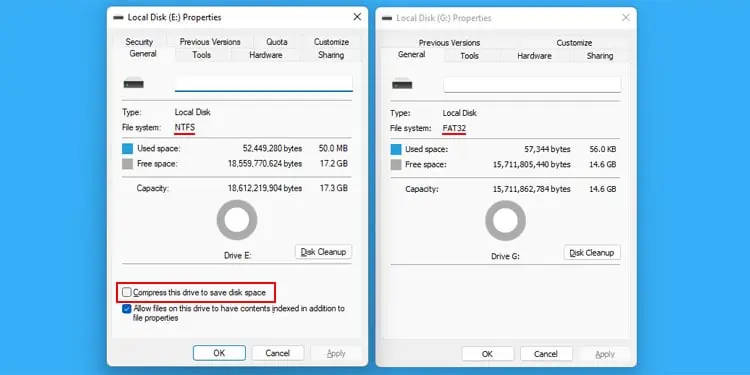
NTFS also supports transparent compression on its files. You cancompress particular filesor all the files inside a partition or a directory.
Afterward, the file compression will occur whenever you save or write any data to the folder or drive where compression is enabled. While opening the NTFS compressed files within Windows, the file system decompresses only the necessary portions and loads them into the memory. So, there’s no loss of performance while you are using these files.
Unlike NTFS, FAT does not support the compression of files.
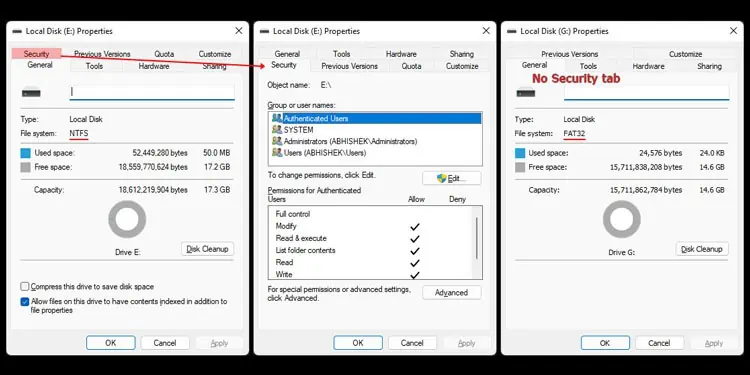
Security
FAT file systems do not provide anything in terms of security, whereas NTFS contains two separate features to protect your files and folders. They are Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Encryption File System (EFS) technology.
ACL technologyspecifies two types of permission on a file/folder,
The read/write permissions determine which user account or user group can read or modify the file/folder. But only the user account or group who is the current owner can change the permissions. So, this feature allows different levels of access for different folders and restricts others from making undesirable changes to the system and other data.
EFS technologyallows encryption on NTFS drives. So, only the device which has the encryption keys can access the drives. Even if someone has physical access to the storage disks, they won’t be able to access their contents from another computer or other devices.
Backup
NTFS drives support a technology calledShadow CopyorVolume Snapshot Service (VSS).With this feature, you can take a snapshot of your partition or files and save them as a backup. This process also saves security information like ACL permissions, file linkage, and other hidden data, which is impossible by using the usual copy/paste features.
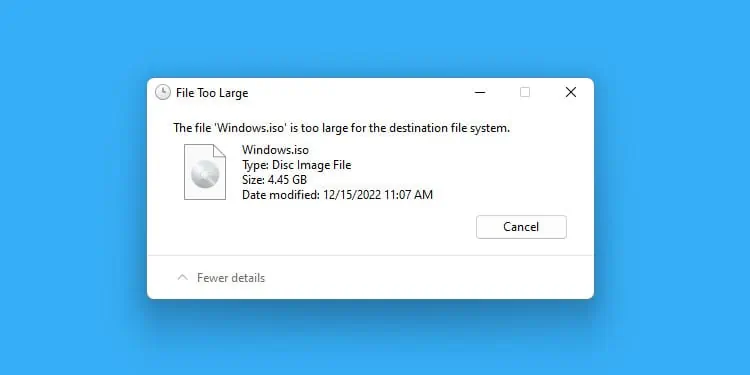
FAT32 file systems do not support such features. The only way to create backups to FAT32 drives while preserving those hidden data (from internal NTFS drives) would be to archive the files using third-party software. You will also need to archive them into multiple 4 GB or less chunks to be able to store them.
File Organization
FAT32 file system does not provide many options in terms of file organization other than the usual nested folder and file structure. On the other hand, the NTFS file system includes many other additional features for a flexible and more efficient file organization, such as:
Conversion
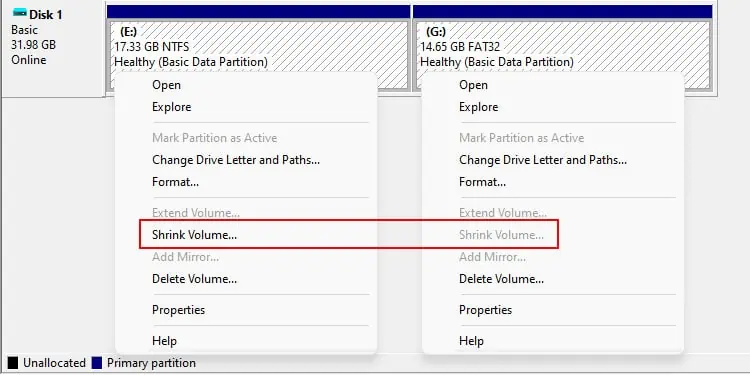
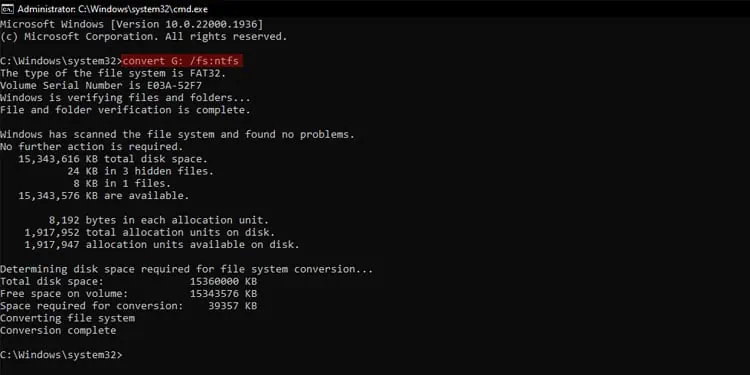
Windows allows converting FAT32 to NTFS using theconvertcommand without losing any data. But you will need to format an NTFS drive to convert it to FAT32 with built-in methods.
Which One Should You Use?
While NTFS is generally the better choice, there are some specific situations where you need to use FAT32:
NTFS is the best option for all other situations as it provides better reliability, security, and various other features.
It is especially true for your internal drives (larger than 512MB), where you should never use any FAT file system. On Windows, FAT systems will never provide all the necessary features and support that NTFS can. Similarly, other operating systems have their own file systems that are most compatible and efficient with their OS.