If you encounter any system issues on Windows and browse the internet for fixes, people will suggest you use DISM, SFC, or CHKDSK tools. While all these utilities are used to repair system corruption in Windows, they target different types of corruption—SFC repairs corrupted system files, DISM repairs Windows Image, and CHKDSK fixes errors with the disk.
So, you might want to know more about them to determine if they work or not. We’ll talk about these utilities in detail in the later sections. And, we’ll also provide you with suggestions on when you should choose a particular one.
System File Checker (SFC)
The System File Checker is the most common Windows utility used to scan for any corrupted system files and repair them. SFC works together with the Windows Resource Protection (WRP) feature and uses the Component Store (WinSxS folder inside the Windows folder) to perform the repairs.
The component store tracks the system files, directories, registry keys, and services and helps in the restoration of any corruption or boot failures in the system files.
When you run SFC, WRP checks whether the system files are in the correct location. It also checks whether the files have the correct hash encryption by comparing them and hard links with the COMPONENTS (hidden) registry hive data.
If it detects any integrity violation, it uses the files inside WinSxS or WinSxS/Backup to replace the files and restore any broken hard links.

So, you should run SFC whenever you encounter any system issues.Basically, if any protected files like drivers, default programs and tools, or services don’t work, consider run SFC.
How to Run SFC?
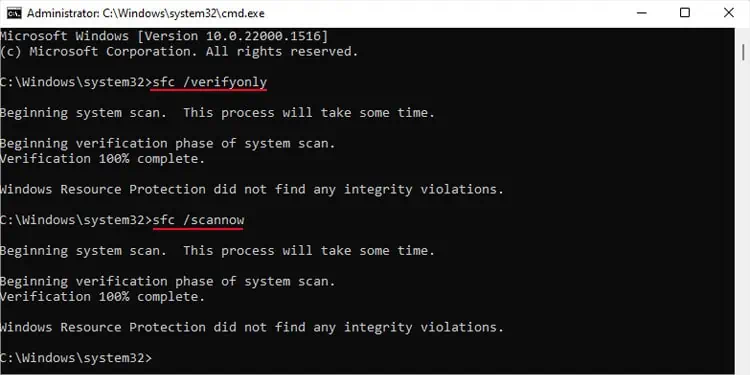
You can use the Elevated Command Prompt to run the System File Checker.
After running the sfc /scannow command, you may get one of three results:

If WRP couldn’t repair the corrupt files, it indicates that the component store itself is suffering from some errors. In such cases,you need to run DISM first as this utility restores health of the component store.
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM)
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) allows varieties of functions in Windows. One such use is to repair an online or offline Windows image.
The offline image means an image of a Windows system stored in.wimor.esdfile. It can also be.vhd,.vhdx, or other virtual disk files that store the image. The online image refers to the active operating system and it basically includes the Windows Component Store.

You need to use one of three switches with theDISM /Cleanup-Imagefunctionality, /Checkhealth, /Scanhealth, and /Restorehealth.
By default, when you use DISM to repair a Windows image, it checks the component store for corruption using the data in the registry and the hash signature of the files.
If it detects any corruption, by default, it uses the Windows Update (WU) client to get the files necessary from the WU server to fix the corruption. But you can also use other sources by setting them manually or changing the default source in your Group Policy settings.
You must be connected to the internet to use Windows Update as the source. If not, it can only check for corruption but can’t fix them. It is always recommended torun DISM if SFC can’t resolve any system issue. Also, DISM only repairs the Windows image, so you should alsorun SFC again after running DISMto fix other system files.
How to Run DISM?
You also need to use command line interfaces like theCommand Promptto run DISM. If you don’t manually specify any source, it automatically uses the default one.
If you are not connected to the internet, you need to provide a manual source to be able to run the restore health command.
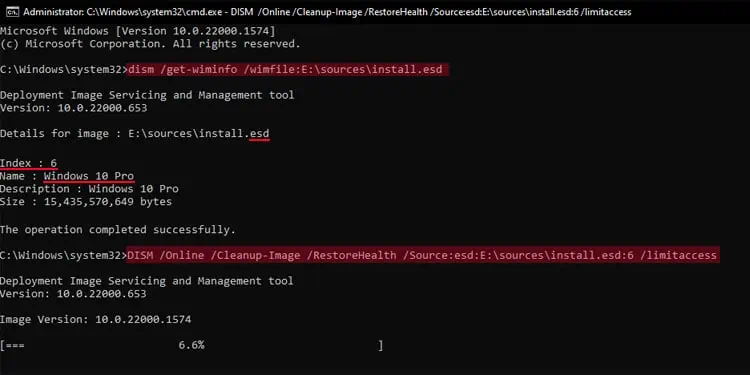
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:wim:E:\sources\install.wim:1 /limitaccess
Here,/limitaccessprevents DISM from using the Windows Update.
You need to replace the path and type of Windows image (wimoresd) as well as the index number (1 in the above example) with the appropriate parameters.
If you don’t know the index number, use the commanddism /get-wiminfo /wimfile:E:\sources\install.wimand check the number for your Windows version.

If you need to use DISM to check and fix an offline Windows image, such as from the Windows Recovery Environment, you need to replace/onlinewith/image:“path to offline image”while also providing amanual source.
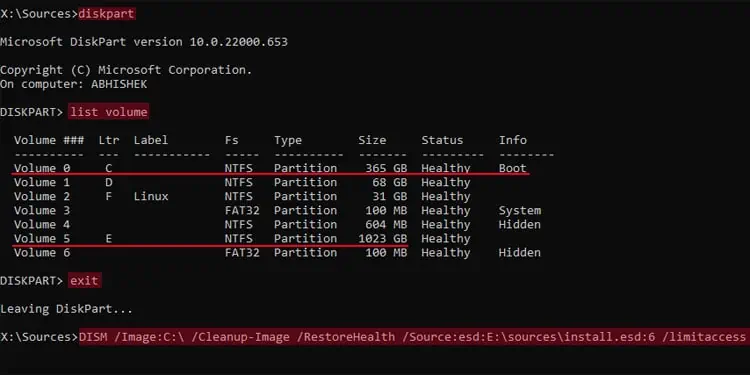
The recovery environment also rearranges the drive letter, so you need to figure them out by using thediskpartcommand to specify the path for the/Imageand the/Source
The command would look like this:
DISM /Image:C:\ /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:esd :E:\sources\install.esd:6 /limitaccess
If you are running DISM from the recovery environment, it’s best to run SFC as well. Similar to DISM, you need to add other parameters to run this program in an offline environment. Here’s the command:
SFC /Scannow /offbootdir=C:\ /offwindir=C:\windows
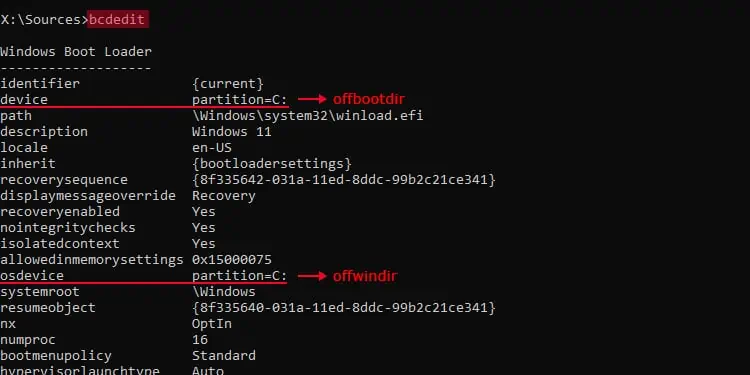
Here, theoffbootdirrepresents the drive with the boot files andoffwindirrepresents the drive with Windows OS. They may not beC:or even the same letter in the recovery environment, so you need to replace them accordingly.
Run thebcdeditcommand and look fordeviceandosdeviceunder Windows Boot Loader for the respective values.
Disk Checking (CHKDSK)
TheDisk Checking Utility (CHKDSK)checks the disk for any file system or sector-level corruption. You need to run this tool wheneveryou encounter any disk or file system-related errors, such as copy/paste functions not working, an external drive not opening, and so on.
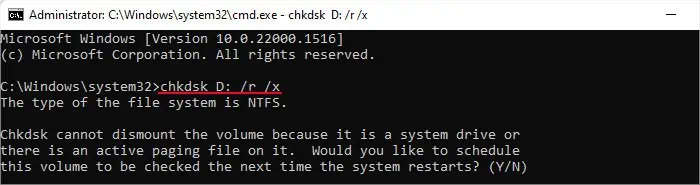
CHKDSK works by checking the file system and partition metadata to look for logical and physical disk corruption. You can only check one partition or drive at a time. And if you don’t specify any drive, it checks your system drive (usually C:).
Depending on your need, you need to use separate flags with the CHKDSK command. If you don’t use any flags, it only checks the drive for errors but doesn’t attempt to fix them. Some important flags are:
How to Run CHKDSK?
You can run the Disk Checking utility using a graphical interface by going to a drive’s properties. However, it does not give you different options for customizing the scan and repair process. So, it’s better to run this utility using the Command Prompt.
When to Run DISM, SFC, and CHKDSK?
To summarize these utilities,SFC repairs all protected system filesfor any corruption and uses the Windows Store components as a repair source. And DISM checks your component store for corruption and repairs it using the Windows Update.
So you should try running the SFC whenever you encounter any system issues. If SFC doesn’t run properly or can’t resolve your issue, run DISM and then SFC again.
As for CHKDSK, you should run it if the issue you are experiencing is related to storage drives or disks. If you can’t determine the nature of the problem, it’s fine to run all three utilities as they won’t make the issue worse even if they don’t prove useful.