Most of us rely on the Graphical User Interface (GUI) as it’s more convenient than memorizing the traditional command lines. But one thing is certain—you’re able to’t perform every task in the Windows GUI, and that’s when Command Prompt can be at your service.
This built-in command line interface can produce immediate outputs using simple commands with fewer computer resources. This way, you do not have to navigate through different windows just to get a single task done. With this program, you can perform advanced administrative functions or troubleshoot different Windows issues on your own!
In this article, I will discuss 50 commands you must know to master Command Prompt. But if you’re relatively new to this utility, I advise checking ourbeginner’s guidefirst.
Basic Commands
Before deep diving into the major commands, I’ll start with the basic ones. Whether you’re planning to use Command Prompt extensively or just for general purposes, these are going to be useful.
CLS
This command simplyclears the Command Prompt screen. If you feel toclear up the working spaceafter executing too many commands, it can be extremely helpful. All you have to do is typeclsand hit Enter.
Exit
If you’re planning toclose the Command Promptapplication, you do not require moving the cursor to press the Close button. Simply run the exit command and the program quits.
you’re able to also use the/bparameter toexit from the loaded batch script. This way, the main window remains open and only the batch file is exited. However, if you use the parameter outside the script, it will close the CMD app.
Help
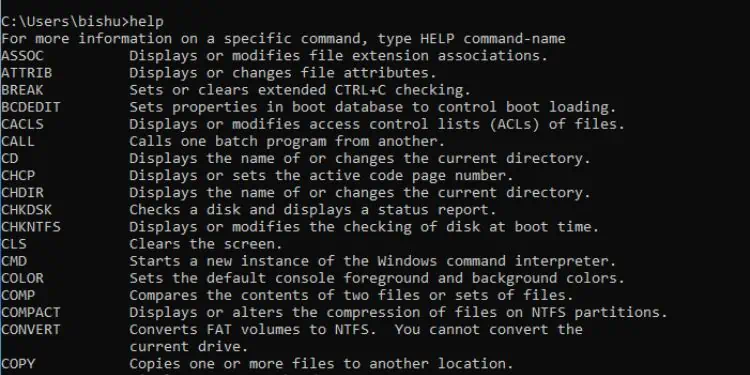
This command comes in handy if you come across any command and wish to know its function. It provides you with thesyntax along with the different parameters(switches).
If you simply execute help, it displays a list of the common commands used in Command Prompt.
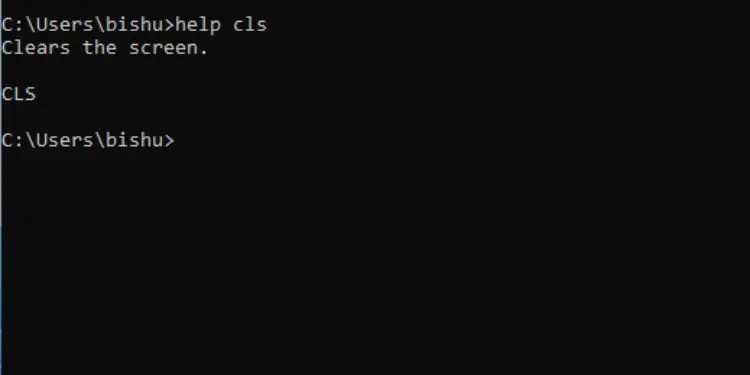
However, not all commands support this utility. In that case, you may use the/?parameter and this should work for every command.
CD or CHDIR
It simply means ‘Change Directory’ and as the name suggests, itswitches you from the current directorybased on the specified path.
If you simply execute cd, it will just display the name of your current directory. Therefore, it’s important to learn the different parameters along with their functions and syntax:
Clip
This commandcopies the outputexecuted from a certain command into the Windows clipboard. In this way, you can directly copy the data into any other program.
It’s extremely useful to directlycopy the text or script fileswithout opening them. Here are the parameters associated with it:
Ver
Command Prompt offers the quickest way toview the version number of Windowsusing a simple command. This way, you can determine whether the latest Windows version is installed on your computer.
System Commands
Whether you’re trying to learn about your computer or perform some system-related tasks, the following commands can come in handy:
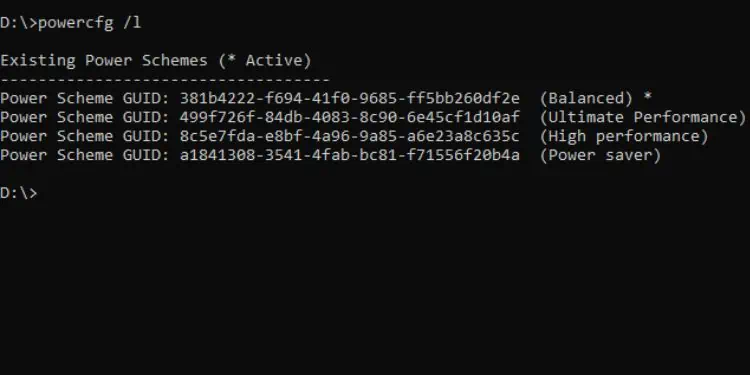
Powercfg
This Command Prompt utility allows you tocontrol the overall power settingsof your computer. Note that if you use it without the appropriate parameters, you’ll encounter an “Invalid parameters” error.
While there are plenty of parameters available, I’m only going to discuss the most common ones below. If you want to learn more, simply executepowercfg /?.
To learn the above commands in detail, I recommend executing thepowercfg /? command.
For example, if you wish to know more about the/listparameter, you can executepowercfg /list.
Shutdown
Interestingly, you canturn off your computerusing a single command on Command Prompt. Also, it’s possible to schedule the shutdown process as you desire.
Here are some common parameters that might be useful:
Driverquery
Moving on, device drivers are integral components of a computer. If you seek information on them, we already have the Device Manager utility on Windows GUI.
However, if you wish to display detailed driver information while working on the command-line interface, you may simply typedriverqueryand hit Enter.
Along with that, you can utilize the following parameters each having individual functions:
Hostname
This commandprints the device name. If you’re unsure about yours or you’re trying to identify it on another computer, simply typing hostname and pressing Enter in the Command Prompt will display the result.
Systeminfo
Unlike the hostname command, this willprint detailed information about your computer.Basically, it’s like launching the System Information application tocheck your PC specs.
Moreover, you can use the same parameters used indevicequery(/s, /u, /p, /fo, /nh, /si, and /v) to print the output in your desired format.
Windows Troubleshooting Commands
If you’re facing a Windows-related issue, there could be several causes for it—corrupted drive, system files, images, or more. Usually, running useful troubleshooters and commands can fix the problem, and that’s exactly what I will cover in this section.
CHKDSK
This command checks for the local disks on the computer and informs users aboutlogical and physical errors. Note that fixing errors is only possible if you use the following parameters wisely.
Here, I have only discussed the common ones. But if you want to learn more, here’s a complete guide on how to runCHKDSK to repair and fix a hard drive.
SFC
The Windows System File Checker (SFC) helps yourepair corrupted Windows files. It works by replacing corrupted files, which can even optimize the computer’s performance.
Here are some of the most used SFC commands:
DISM
This command starts the Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool to configure thefeatures and packages of Windows images. There are plenty of DISM commands to use when troubleshooting Windows, including FFU, WIM, Imaging, and more. But I will only be discussing the common parameters.
For your comfort, we have already provided a detailed guide onrunning different DISM commands.
msdt.exe -id DeviceDiagnostic
TheHardware and Devices troubleshooteris no longer available with the other troubleshooters in Windows Settings. However, the utility can find and fix related problems with all hardware components.
In Windows 11, you may launch it using themsdt.exe -id DeviceDiagnosticcommand on Command Prompt.

File and Directory Management Commands
Managing files and directories on Command Prompt can be a little tricky. Nevertheless, here are some of the basic commands that can make your tasks a lot easier.
DIR
This commanddisplays all the files and directories/subdirectoriesfrom the specified drive/directory.
Most users utilize this command to list the files and directories. This is possible by simply executing the dir command. Along with the listings, it also displays the volume’s label, serial number, and the total number of files and directories.
Apart from that, you can also utilize the following parameters:
Copy
As the name suggests, this commandcopies the files from one location to another. Note that it will just create a duplicate instead of moving it.
For example, to copy theexample.txtfile from the D drive to the Example folder in the same drive, here’s the command I’ll use:
copy example.txt Example
Move
This command functions the same way ascopy. However, the difference is that it actuallymoves the file from one location to the other. It’s basically the cut-and-paste technique we use in Windows GUI.
For example, to move theexample.txtfile from the D drive to the Example folder in the same drive, here’s the command I’ll use:
move example.txt Example
Del or Erase
Both the Del and Erase commands can be used topermanently delete a file. This means that you can’t retrieve the file back from the Recycle Bin.
For example, to delete theexample.txtfile permanently, here’s the command I’ll execute:
del example.txt
MKDIR or MD
Both the MKDIR and MD commands are used tocreate a new directory (folder). you may do this in the present directory or even on another directory directly, meaning you do not require moving to that specific drive/directory to create one.
For example, if I’m in D drive and wish to create a new directory, here’s the command I’ll use:
mkdir MyDirectory
But if wish to create a new directory in a specific path, here’s what I would execute:
mkdir C:\Users\bishu\Desktop\MyDirectory
Rename or Ren
Ren orRename commandsimplyreconfigures the file or directory name. While doing so, ensure you do not duplicate the name with any other file/directory.
Taking the same example as above, here’s how I am going to rename the two files I had created earlier:
ren C:\Users\bishu\Desktop\MyDirectory MyDir
RMDIR or RD
It stands for‘Remove Directory’and that’s exactly what the command does. You may also use a shorter command that performs the same action–RD.
Here are all the parameters for the RMDIR command:
As an example, I’m going to show you how to delete the MyDirectory file that I created earlier:
rmdir MyDir
rmdir C:\Users\bishu\Desktop\MyDir
Type
This command is used todisplay a text file’s contenton Command Prompt. This way, you do not have to navigate to a certain location, open the file, and again close it if not necessary.
Assoc
This command is used todisplay or manage different file name extension associations. Note that you require administrative privilege to modify the associations.
If you simply execute the assoc command, the command-line utility lists all the extensions along with their associated file types.
Also, you may check which file extensions are associated with individual file types. For example, you can find out all the extensions that are associated with ‘sysfile’ as shown in the below example.
Example:assoc | find “sysfile”
It’s possible to modify the associations too. You can associate any file extension to whichever file type you want.
Example:assoc .abc=sysfile
Lastly, you may even delete an association. However, you’ll need to restart your computer to apply the changes.
Example:assoc .abc=
FC
FC stands for “File Compare” and as it sounds, it’s used forcomparing two filesso that you can learn about their differences. As shown in the demonstration above, I have compared two text files to know the item difference inside them.
Here are some of the useful parameters for the FC command:
Attrib
This commandmanages the attributes for files and folders. You can set whatever attribute you wish—Hidden, Read-Only, System, and more. To set an attribute, use ‘+’ and to remove, use ‘-’.
Tree
If you’re wishing to view the subdirectories inside of a directory or a drive,the tree command will make itlook graphically pleasing. It structures the document in an easy-to-view format. All you have to do is run the tree command and specify the path if required.
Below are the two parameters you can adopt with the tree command:
Disk/Drive Management Commands
Along with file and directory management, it’s also possible toconfigure disks and drivesin Command Prompt.
Here are the 7 most used commands for this purpose:
Vol
This is a command to quicklycheck the volume name or serial number. All you have to do is executevolwith the drive letter.
Format
While there already exists easy-to-use GUI applications forformatting your disk drives, it’s never a bad idea to learn this on Command Prompt.
If you want to format a hard drive having just one partition, the format command should work out for you. However, the better option would be usingdiskpart, which I shall discuss below.
Here, I’ll only mention the common parameters. Nonetheless, you can go through the other guide that should help youformat a hard drive from CMDin detail.
Diskpart
This is a command-line interpreter that offersdisk management featureson Command Prompt. With this utility, you can assign drive letters, manage the drive attributes, configure partitions, display disk information, format a drive, and much more.
Typediskpartand this should launch the interpreter. However, you require administrative privilege to use it.
In the table below, I have mentioned the most used commands in Diskpart. If you wish to learn more about disk partitions using thediskpartcommand, you can check out our dedicated guides for bothHDDandSSD.
Defrag
Defragmentation simply meansreorganizing the data inside an HDDto achieve better performance (not recommended on SSD).
Like any other action, Windows already offers a dedicated utility.
However, if you wish to know this in detail, Command Prompt offers tons of parameters that should help you out. Note that this command requires administrative privilege.
Diskusage
This might not be the most used command but is definitely worth it. you’re able to get thesummarized details on the selected disk’s usagein no time.
Simply executing thediskusagecommand should do the job (note that you need to open CMD as an administrator). Along with that, you can take a look at the following parameters that might be beneficial:
Networking Commands
Unlike others, networking commands are widely used mainly for troubleshooting purposes. In fact, fetching IP addresses or configuring network settings is much easier on Command Prompt than using GUI components.
If you’re a networking enthusiast, here are the commands that you need to focus on:
Net
you’re able to use this command to manage different networking services. It comes with multiple options each performing a specialized task.
Here, I’ve only mentioned the most common ones. you may execute thenetcommand without a parameter to get more.
Ipconfig
This command is fornetwork configuration and management. You can view the detailed Windows TCP/IP information, release/renew IP addresses,flush the DNS cache, and much more.
Executingipconfigwithout parameters displays the IPv4, IPv6, subnet mask, and default gateway for every adapter. For other purposes, you can adopt the following parameters:
Netsh
This is another essential networking command used formanaging network configurations. You can executenetshto launch the dedicated shell. After that, you can perform desired networking operations using some of the well-known parameters from the below table:
Netstat
This commandlists the active connectionson your computer. It displays the protocol, local as well as foreign address, and the current state. Just executing thenetstatcommand will list the active TCP connections.
To display other protocols, here are some parameters you can use:
Ping
This command is widely used fortesting host-server reachability and internet connectivity. Executingpingdisplays the IP address statistics and the approximate round trips in milliseconds.
Here are a few parameters that I recommend trying out:
Tracert
This commandtraces the route to a certain IP or domainby sending ICMP or ICMPv6 messages with increasing TTL values. It’s extremely useful during network troubleshooting as it informs users about the routing issues and validates the network paths.
Implementing thetracertcommand without a parameter traces the route of the specified domain/IP over a maximum of 30 hops.
Nevertheless, you could make use of the following parameters to gain additional networking information:
Pathping
This command is acombination of Tracert and Ping. When executed without a parameter, it traces the route to the target over a maximum of 30 hops and computes statistics for 125 seconds (by default).
Here are some of the most usedpathpingparameters:
Getmac
If you wish toget the MAC addressof your computer, you can execute thegetmaccommand and this will display the result in no time. The result includes both the physical address and the transport name.
Along with that, I highly recommend trying out the following parameters:
NSLookUp
This is yet another command-line utility that includes numerous commands toobtain domain name or IP address information. To start the prompt, simply typenslookupin the Command Prompt and hit Enter.
While there are countless parameters fornslookup, I’m only going to focus on a few common ones in the table below:
Miscellaneous
If you have implemented each of the commands I’ve discussed, you should now be proficient enough to use Command Prompt. However, the aforementioned commands are not enough to master this Windows command-line interface.
There are thousands more, and it’s impossible for me to include all of them in this single post.
For now, I would recommend trying out the following commands that could come in handy while you’re on the way to mastering Command Prompt:
Tasklist
You can use this command todisplay the currently running processeson your computer. Executingtasklistlists down the name of the process, its PID, session name, session number, and memory usage. Also, you can try out the following parameters:
Taskkill
While thetasklistcommand displays the processes,taskkillkills/ends them. You can use either process ID or image name to do this task. Therefore, you need to utilize any of the following common parameters:
Powershell
If you prefer WindowsPowerShell over CMD, you can actuallyrun the Command Prompt as a Powershell window. Just typepowershelland hit Enter. You’ll likely get the PS prefix indicating that you can now run all the Powershell cmdlets here.
Set
This command is used forconfiguring theWindows environment variables. To display all the available ones, you may use thesetcommand without any parameters. In order to set a new environment variable, you can use a variable name and provide the necessary value.
Likewise, it’s possible to delete any environment variable too. Below is the syntax that should clear your doubt.
Thesetcommand on Command Prompt has the following two parameters with individual functionality:
Start
You can use this command tolaunch a new Command Prompt window. Without the use of any parameter, it will simply launch the new prompt. However, utilizing the following parameters can help you perform just more than that:
BCDBoot
Most users utilize this command torepair the boot environmentfrom the Windows Recovery Environment. It works by copying the Windows installation files to a system partition. You need to executebcdbootwith the following parameters:
Date
This is another useful command toquickly check the current date. You can display or set a new date as per your requirement. If you execute just thedatecommand, the prompt displays the date and asks you to set a new one. But if you quickly want to check the date, use the/tparameter.
Prompt
This commandoffers customization of the textthat appears in front of the cursor (by default, it’s the current directory path).
You can change this to any character string of your choice or predefined characters (like current date, drive, path, times, windows version, etc.) using special codes. You can check using the/?Parameter. To switch back to the normal format, execute the prompt without any parameters.
Color
Certainly, you have thought of customizing the Command Prompt. To your surprise, it’s possible to tweak the default black (background) and white (foreground/text) combination. For this, you require specifyingtwo hex digits—the first representing the background and the second corresponding to the text.
As per the above table, let’s say you want a red background with light blue text. So, you’ll have to execute the following command:color 49
While you’re at it, note that you cannot set the same background and foreground colors. Even if you do it, the command will not execute and you’ll be left with the existing combination.
To switch back to default, run the color command without any parameter.